Your position: Home
/
wdm-optical-network
wdm-optical-network
Talk about CWDM&DWDM Optical Network
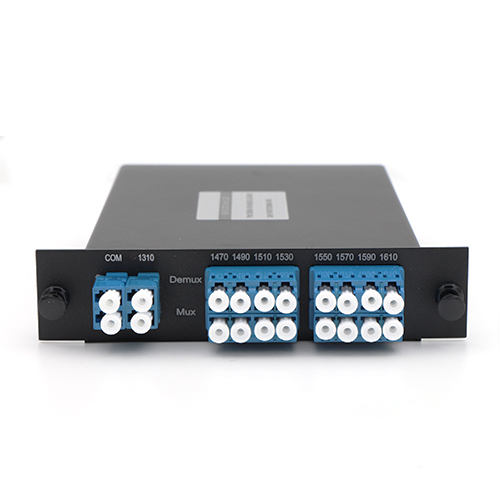
WDM (Wavelength Division Multiplexing) is a concept that describes combination of several streams of data/storage/video or voice on the same physical fiber optic cable by utilizing several wavelengths (or frequencies) of light with each frequency carrying a different sort of data. There's two types of WDM architectures: CWDM (Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing) and DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing). CWDM systems typically provide 18 wavelengths, separated by 20 nm, from 1470nm to 1610nm according to ITU-T standard G.694.2. However, for different applications, there are different ITU-T standard to define the specific wave range and channels. Compared to CWDM, DWDM is defined in terms of frequencies. Some DWDM network systems provide up to 96 wavelengths, typically without any more than 0.4 nm spacing, roughly over the C-band range of wavelengths.
Now, here we will talk something about cwdm&dwdm optical network.
CWDM Technology
CWDM is proved to be the initial access point for many organizations due to its lower cost. Each CWDM wavelength typically supports as much as 2.5 Gbps and could be expanded to 10 Gbps support. This transfer rates are sufficient to aid GbE, Fast Ethernet or 1/2/4/8/10G Fibre Channel, along with other protocols. The CWDM is limited to 16 wavelengths and is typically deployed at networks as much as 80 km since optical amplifiers can't be used due to the large spacing between channels.
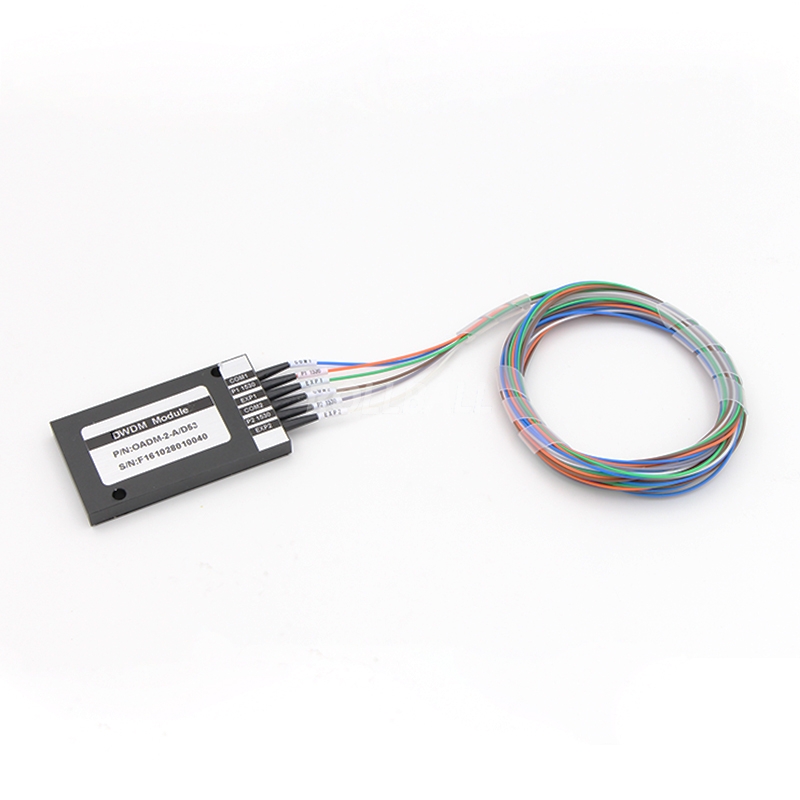
DWDM Technology
DWDM is a technology allowing high throughput capacity over longer distances commonly ranging between 44-88 channels/wavelengths and transferring data rates up to 100 Gbps per wavelength. Each wavelength can transparently have a wide range of services. The channel spacing from the DWDM solutions is defined by the ITU standards and can range from 50 GHz and 100 GHz (the most widely used today) to 200 GHz. DWDM systems can provide up to 96 wavelengths (at 50 GHz) of mixed service types, and can transport to distances up to 3000 km by deploying optical amplifiers (e.g., DWDM EDFA) and dispersion compensators thus enhancing the fiber capacity with a factor of x100. Due to its more precise and stabilized lasers, the DWDM technology tends to be more expensive in the sub-10G rates, but is really a more appropriate solution and it is dominating for 10G service rates and above providing large capacity data transport and connectivity over long distances at affordable costs.
WDM (Wavelength Division Multiplexing) is a concept that describes combination of several streams of data/storage/video or voice on the same physical fiber optic cable by utilizing several wavelengths (or frequencies) of light with each frequency carrying a different sort of data. There's two types of WDM architectures: CWDM (Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing) and DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing). CWDM systems typically provide 18 wavelengths, separated by 20 nm, from 1470nm to 1610nm according to ITU-T standard G.694.2. However, for different applications, there are different ITU-T standard to define the specific wave range and channels. Compared to CWDM, DWDM is defined in terms of frequencies. Some DWDM network systems provide up to 96 wavelengths, typically without any more than 0.4 nm spacing, roughly over the C-band range of wavelengths.
Now, here we will talk something about cwdm&dwdm optical network.
CWDM Technology
CWDM is proved to be the initial access point for many organizations due to its lower cost. Each CWDM wavelength typically supports as much as 2.5 Gbps and could be expanded to 10 Gbps support. This transfer rates are sufficient to aid GbE, Fast Ethernet or 1/2/4/8/10G Fibre Channel, along with other protocols. The CWDM is limited to 16 wavelengths and is typically deployed at networks as much as 80 km since optical amplifiers can't be used due to the large spacing between channels.
DWDM Technology
DWDM is a technology allowing high throughput capacity over longer distances commonly ranging between 44-88 channels/wavelengths and transferring data rates up to 100 Gbps per wavelength. Each wavelength can transparently have a wide range of services. The channel spacing from the DWDM solutions is defined by the ITU standards and can range from 50 GHz and 100 GHz (the most widely used today) to 200 GHz. DWDM systems can provide up to 96 wavelengths (at 50 GHz) of mixed service types, and can transport to distances up to 3000 km by deploying optical amplifiers (e.g., DWDM EDFA) and dispersion compensators thus enhancing the fiber capacity with a factor of x100. Due to its more precise and stabilized lasers, the DWDM technology tends to be more expensive in the sub-10G rates, but is really a more appropriate solution and it is dominating for 10G service rates and above providing large capacity data transport and connectivity over long distances at affordable costs.
 USD
USD EUR
EUR GBP
GBP CAD
CAD CNY
CNY SAR
SAR SGD
SGD NZD
NZD ARS
ARS INR
INR COP
COP AED
AED